Infantile cerebral palsy (ICP)
Infantile cerebral palsy (ICP) is a usually spastic disturbance of the nervous and muscular system that begins in childhood. It is characterised by disturbances of the nervous and muscular system in the areas of muscle tension (tonus), muscle strength, coordination and movement patterns. Spastic hybrid forms with generally elevated muscle tension are the most common.
Causes
The causes of infantile cerebral palsy can vary widely. A lack of oxygen, umbilical cord complications, infections, cerebral bleeding and accidents can lead to infantile cerebral palsy throughout pregnancy, but most frequently in the course of birth.
Multiple disabilities are seen in most cases. It occurs in 3 out of every 1,000 live births. However, premature infants are affected most frequently.
Symptoms
The symptoms of infantile cerebral palsy vary widely and can be highly defined individually. Spastic symptoms occur in 75% of all cases.
- Hemiplegia (32%): here the limbs on one side of the body are affected, the arms usually more severely than the legs.
- Diplegia (40%): the legs are more severely affected than the arms.
- Tetraplegia (2%): in tetraplegia, all limbs are paralysed; motor and mental development is significantly delayed. Only about 10% of affected individuals are able to walk.
- Bilateral hemiplegia: spastic paralysis of all four limbs, with the arms more severely affected than the legs.
- Triplegia: spastic paralysis of three limbs.
In all forms, the long flexors and the adductors in particular are affected by paralysis. Spasticity also causes stiffening of the joints. Typical clinical pictures of the individual joints can be described as follows: the hip is flexed, angled and rotated inward. There is a tendency towards stiffness in the flexion position of the elbow, wrist joint and knee joint. The forearm is bent and the thumb is rotated inward. The ankle and foot are in the equinus position and the spinal column is severely bent as well.
Diagnosis and therapy
ICP is diagnosed on the basis of clinical findings after other progressive causes such as tumours or inflammation have been excluded. Treatment is focused on multidisciplinary therapy derived from various medical, orthopaedic and therapeutic approaches. Here Ottobock offers a variety of medical devices ranging from products for infants to adults, for example to help with posture and positioning as well as improving balance and the ability to walk (lower leg orthoses, walking aids, sitting and positioning aids).
Products

Carbon Ankle Seven
Carbon Ankle Seven carbon springs make it possible to build ankle foot orthoses of particularly low weight that are also able to withstand high dynamic loads.

Cosa Active/Junior
The Cosa Active/Junior is a hip abduction orthosis which stabilises the standing and sitting base and provides improved torso control.
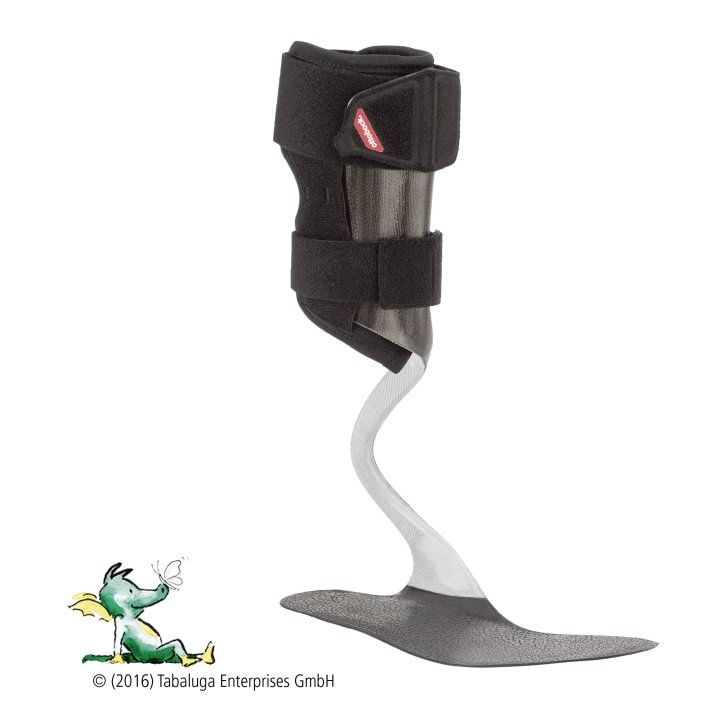
WalkOn Reaction junior
Children who have minor paralysis of the lower limbs wear the WalkOn Reaction junior. It uses the ground reaction force to support dorsiflexion and the knee joint. The orthosis can be used from shoe size 24.

For families on the go
The right devices for visiting grandparents, taking a walk and doing shopping. The following devices make transport easier for you.
The products shown are fitting examples. Whether a product is actually suitable for you and whether you are capable of exploiting the functionality of the product to its fullest depends on many different factors. Amongst others, your physical condition, fitness and a detailed medical examination are key. Your doctor or orthopaedic technician will also decide which fitting is most suited to you. We are happy to support you.
